How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a question many aspiring pilots ask. This guide delves into the intricacies of drone operation, from understanding basic controls to mastering advanced techniques. We’ll explore legal regulations, essential safety procedures, and the nuances of various drone models and their capabilities. Whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to enhance your existing skills, this comprehensive resource will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to take to the skies responsibly.
We will cover everything from pre-flight checks and choosing the right drone for your needs to mastering advanced maneuvers and understanding essential maintenance. We’ll also explore the exciting world of aerial photography and videography, helping you capture stunning images and videos from unique perspectives. By the end, you’ll be well-prepared to embark on your drone piloting journey with confidence and a strong understanding of safe and responsible operation.
Drone Regulations and Safety
Operating a drone responsibly involves understanding and adhering to both legal requirements and crucial safety procedures. Failure to do so can result in accidents, fines, and legal repercussions. This section covers essential aspects of safe and legal drone operation.
Drone Laws and Regulations
Drone regulations vary significantly across countries. In the United States, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) requires drone registration for certain models and mandates adherence to specific flight rules, including limitations on altitude, flight distance from airports, and operation in controlled airspace. Similar regulatory bodies exist in other countries, each with its own set of rules. Before flying, always research and understand the specific laws and regulations in your location.
These regulations often cover aspects like airspace restrictions near airports and other sensitive areas, weight limits for drones, and requirements for pilot certifications.
Pre-Flight Safety Checklist
A thorough pre-flight inspection is crucial for safe operation. This checklist ensures all systems are functioning correctly and minimizes the risk of accidents.
- Inspect the drone’s propellers for damage or debris.
- Check the battery level and ensure it is fully charged.
- Verify GPS signal strength and accuracy.
- Confirm the drone’s connection to the controller and mobile application.
- Test all control inputs to ensure proper functionality.
- Review the weather conditions and ensure they are suitable for flight.
- Identify and avoid potential hazards in the flight area, such as obstacles, power lines, and people.
In-Flight Safety Procedures
Maintaining situational awareness and adhering to safety protocols during flight is paramount. This includes maintaining visual line of sight with the drone, avoiding crowded areas, and being prepared for unexpected events.
Post-Flight Safety Procedures
Post-flight procedures are equally important for the long-term health and safety of the drone and its operator. Proper storage and maintenance help to extend the lifespan of the drone and prevent accidental damage.
- Power down the drone completely.
- Carefully remove and store the propellers.
- Inspect the drone for any damage sustained during the flight.
- Clean the drone’s body and propellers to remove any dirt or debris.
- Store the drone in a safe, dry place.
- Charge the battery according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Handling Unexpected Situations

A flowchart helps to visualize the decision-making process for handling unexpected events during flight, such as low battery, loss of signal, or unexpected weather changes.
Flowchart: The flowchart would begin with a “Problem Detected” box, branching to various scenarios (e.g., low battery, loss of signal, strong wind). Each branch would lead to specific actions (e.g., initiate Return-to-Home, land immediately, seek shelter). The flowchart would conclude with a “Problem Resolved” or “Emergency Landing” box, clearly outlining the steps for each possible scenario. The decision points would be based on factors like remaining battery life, proximity to the home point, and the severity of the unexpected event.
Choosing and Setting Up Your Drone
Selecting the right drone and setting it up correctly are essential steps for a successful flight experience. This section guides you through the process of choosing a drone based on your skill level and setting it up for its first flight.
Choosing a Drone Model
Drone models vary widely in features, capabilities, and price points. Beginner drones often offer simplified controls and safety features, while advanced models cater to experienced pilots with more sophisticated flight modes and camera systems. Consider factors like flight time, camera quality, range, and ease of use when selecting a drone.
Setting Up Your Drone
Setting up a new drone typically involves charging the battery, installing the necessary mobile application, and calibrating the drone’s sensors and compass. Refer to the manufacturer’s instructions for specific steps.
- Charge the drone battery fully.
- Download and install the drone’s dedicated mobile application.
- Connect the drone to the mobile application.
- Calibrate the drone’s compass and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) according to the app’s instructions.
- Perform a pre-flight check.
Sensor and Compass Calibration
Accurate sensor and compass calibration are crucial for stable and precise drone flight. Incorrect calibration can lead to erratic movements and inaccurate positioning. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for calibrating these components.
Drone Controller Comparison
Different drone controllers offer varying features and levels of control. The choice depends on individual needs and preferences.
| Controller Model | Pros | Cons | Price Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Generic Basic Controller | Affordable, Easy to Use | Limited Features, Short Range | $20-$50 |
| Mid-Range Controller with Screen | Integrated Screen, More Features, Extended Range | Higher Price | $100-$200 |
| Professional Controller with Advanced Features | Advanced Flight Modes, High Precision, Customizable Settings | High Price, Complex Setup | $300+ |
| Smart Controller with Integrated Camera | Integrated Camera for First Person View (FPV), Advanced Flight Modes | High Price, Requires Mobile Device | $300+ |
Understanding Drone Controls and Flight Modes
Understanding the drone’s controls and flight modes is fundamental to safe and effective operation. This section explains the functions of the controller and various flight modes.
Drone Controller Functions, How to operate a drone
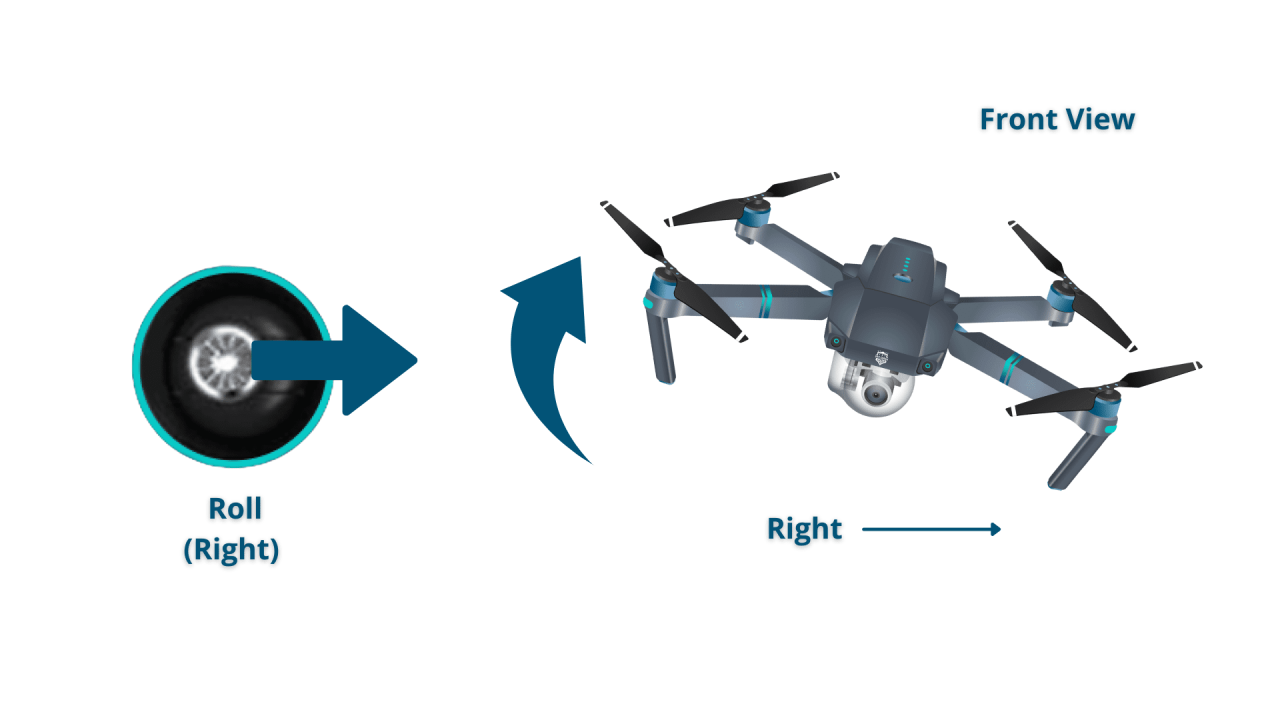
A typical drone controller has two joysticks and several buttons. The left joystick typically controls altitude and yaw (rotation), while the right joystick controls roll (side-to-side tilt) and pitch (forward and backward tilt). Buttons control functions like takeoff, landing, camera control, and flight mode selection. Specific functions vary depending on the drone model.
Flight Modes
Most drones offer multiple flight modes, each designed for different skill levels and flight scenarios. Beginner mode often limits speed and responsiveness, enhancing stability and safety. Sport mode allows for faster and more agile maneuvers, but requires more skill and experience. Other modes may include GPS mode, Return-to-Home (RTH) mode, and cinematic mode for smoother video capture.
Basic Drone Maneuvers
Mastering basic maneuvers is crucial before attempting more complex flights. These include takeoff, landing, hovering, and directional movement. Practice in a safe, open area to build confidence and skill.
- Takeoff: Gently push the left joystick upwards to initiate ascent.
- Landing: Gently push the left joystick downwards to initiate descent.
- Hovering: Maintain a steady position in the air by keeping the joysticks centered.
- Directional Movement: Use the right joystick to control the drone’s direction. Pushing forward moves the drone forward, pushing backward moves it backward, and pushing left or right moves it sideways.
Achieving Smooth and Controlled Movements
Smooth and controlled movements require practice and precise joystick manipulation. Avoid abrupt movements, especially when near obstacles or people. Practice flying in a controlled environment before venturing into more challenging scenarios.
Advanced Drone Techniques and Features
Advanced drone techniques and features enhance flight capabilities and allow for creative aerial photography and videography. This section explores some of these advanced capabilities.
GPS and Return-to-Home (RTH)
GPS enables precise positioning and navigation, while RTH automatically returns the drone to its takeoff point if signal is lost or the battery is low. These features are crucial for safety and ease of use.
Waypoint Navigation
Waypoint navigation allows you to pre-program a flight path for the drone to follow autonomously. This is useful for creating cinematic shots or surveying large areas. The process involves setting waypoints on a map within the drone’s app, defining the order and speed of the flight, and then letting the drone execute the planned path.
Drone Camera Operation
Most drones are equipped with cameras for photography and videography. Understanding camera settings and techniques is crucial for capturing high-quality aerial footage. The process involves adjusting settings like aperture, shutter speed, ISO, and white balance to optimize image quality based on lighting conditions and desired effects. Different drone models have different camera interfaces and functionalities; it is important to consult the manufacturer’s documentation for specific details.
Creative Flight Maneuvers
Creative flight maneuvers add visual interest to aerial photography and videography. Examples include orbiting a subject, following a moving object, and performing smooth, sweeping camera movements. These maneuvers require practice and skill, and should only be attempted in safe environments.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires careful planning and adherence to regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, including safety procedures and legal considerations, consult this excellent resource on how to operate a drone before your first flight. This will ensure you operate your drone responsibly and safely.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting are essential for keeping your drone in optimal condition and extending its lifespan. This section covers routine maintenance procedures and common troubleshooting steps.
Routine Maintenance Schedule
A regular maintenance schedule ensures the drone remains in good working order. This includes cleaning, inspecting, and storing the drone properly.
- Weekly: Inspect propellers, body, and camera for damage; clean any dirt or debris.
- Monthly: Check all screws and connections for tightness; lubricate moving parts (if applicable).
- Quarterly: Perform a more thorough inspection, checking for wear and tear on all components; calibrate sensors and compass.
- Annually: Consider professional servicing if needed; replace worn parts.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Troubleshooting
Understanding common drone malfunctions and their causes allows for effective troubleshooting. This includes issues like low battery, GPS signal loss, and motor failures.
- Low Battery: Charge the battery fully; consider using higher capacity batteries for longer flight times.
- GPS Signal Loss: Ensure clear sky view for GPS signal; avoid flying near tall buildings or dense foliage.
- Motor Failures: Inspect motors for damage; replace faulty motors.
- Propeller Issues: Inspect propellers for damage; replace damaged propellers.
- Controller Issues: Check battery level and connections; try re-pairing the controller with the drone.
Essential Tools and Spare Parts
Having essential tools and spare parts readily available can expedite repairs and minimize downtime.
- Screwdrivers (Phillips and flathead)
- Spare propellers
- Battery charger
- Cleaning cloths and brush
- Multi-tool
- Spare batteries
Drone Photography and Videography Basics
Capturing stunning aerial photos and videos requires understanding basic photography and videography principles. This section provides tips and techniques for improving your aerial imagery.
Principles of Composition and Framing
Effective composition involves arranging elements within the frame to create visually appealing images. Rules of thirds, leading lines, and symmetry are valuable compositional techniques. Framing involves carefully selecting what to include and exclude from the shot to emphasize the subject and create a sense of depth.
Achieving Stable and Smooth Video Footage
Stable and smooth video footage is crucial for professional-looking results. Techniques include using a gimbal, flying smoothly and steadily, and post-processing stabilization.
Camera Settings for Optimal Results
Understanding camera settings such as aperture, shutter speed, and ISO is essential for controlling depth of field, motion blur, and image brightness. Adjusting these settings based on lighting conditions and desired effects is crucial for achieving optimal results. Experimentation is key to understanding how these settings impact the final image or video.
Sample Flight Plan for Aerial Shots
A sample flight plan for capturing landscape shots might involve establishing a high vantage point, then performing slow, sweeping camera movements to capture the expanse of the landscape. For cityscape shots, you might focus on capturing iconic landmarks and showcasing the city’s layout, perhaps using a combination of high-angle shots and close-ups.
Drone Safety and Emergency Procedures: How To Operate A Drone
Understanding emergency procedures and potential hazards is crucial for safe drone operation. This section Artikels steps to take in various emergency scenarios.
Emergency Landing Procedures
Emergency landing procedures vary depending on the situation. If the battery is low, initiate the Return-to-Home (RTH) function if available. If a motor fails or the drone becomes unstable, try to land it in a clear, open area, prioritizing safety over preserving the drone.
Recovering a Crashed Drone

After a crash, carefully inspect the drone for damage. Assess the extent of the damage and repair or replace damaged components accordingly. If the damage is beyond your repair capabilities, seek professional assistance.
Handling Unexpected Situations
Unexpected situations such as low battery warnings and loss of signal require immediate action. Low battery warnings should trigger an immediate return to the launch point. Loss of signal requires a cautious and controlled landing procedure, if possible.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource to begin your journey is this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. From pre-flight checks to mastering maneuvers, understanding the intricacies of drone operation ensures safe and effective flights.
Potential Hazards
A visual representation of potential hazards would depict a variety of obstacles and dangers. This would include power lines (clearly labeled as high voltage), trees, buildings, bodies of water, people (represented as stick figures), and areas with restricted airspace (indicated by a no-fly zone symbol). The illustration would emphasize maintaining a safe distance from these hazards and the importance of visual line of sight.
Mastering the art of drone operation involves a blend of technical skill, responsible decision-making, and a deep understanding of safety protocols. This guide has provided a foundation for your journey, covering essential aspects from legal compliance to advanced flight techniques. Remember that continuous learning and practice are key to becoming a proficient and safe drone pilot. So, take to the skies, explore new horizons, and capture breathtaking moments responsibly.
FAQ Summary
What is the maximum flight time for most consumer drones?
Flight times vary greatly depending on the drone model, battery size, and flight conditions. Expect anywhere from 15 to 30 minutes on a single charge for most consumer drones.
How do I register my drone?
Drone registration requirements differ by country. Check your local aviation authority’s website for specific regulations and registration procedures in your region.
What should I do if I lose control of my drone?
Immediately engage the Return-to-Home (RTH) function if available. If RTH fails, attempt to regain control using the manual controls. If still unsuccessful, prioritize safety and allow the drone to land as safely as possible.
What are the common causes of drone crashes?
Common causes include pilot error (loss of control, poor judgment), battery failure, GPS signal loss, mechanical malfunctions, and collisions with obstacles.
